Self Test Questions Entrepreneurship
Self test questions for the lecture entrepreneurship at KIT.
Session 1: Introduction
What is the activity of an entrepreneur according to Jean Baptiste Say?
The entrepreneur shifts economic resources out of an area of lower and into an area of higher productivity. 🐎
How does Joseph Schumpeter define “entrepreneurship”?
Entrepreneurship is about new factor combinations leading to new products, production methods or new markets. It is about creative destruction. 🤯
What are the career reasons of nascent entrepreneurs? Name and explain them.
- Independence (freedom & control in use of one’s tie) 🗽
- Self-realization (pursue self-directed goals) 🧑🚀
- Financial success (earn money, achieve financial security) 💰
- Recognition (have status & approval by others) 🎖️
- Role (follow family traditions or follow example of others) 👪
- Innovation (accomplish something new) 🚀
What are the motives for starting a business, according to GEM 2019?
Opportunity based entrepreneurship
- To make a difference in the world 🌍
- To build great wealth or very high income
- To continue a family tradition 👪
Necessity based entrepreneurship
- To earn a living because jobs are scarce 📉
Please name the listed five forms of capital and name at least one example.
- Financial Capital 💸
- Money
- Bonds & Security
- Natural Capital 🏞️
- Raw materials
- Pollution absorption capacity
- Land
- Biological yield
- Energy
- Intellectual Capital 🧠
- Human Capital: Skills, Knowledge, Attitude
- Organizational Capital 🏢
- Hardware & Machines
- Software & Databases
- Patents
- Processes & methods
- Social Capital 🫂
- Quality of stakeholder relationship
- Financial Capital 💸
Please give one example of “Creative Destruction” related to entrepreneurship.
A company realizing a customer need not served in the current market. E.g. Apple's IPod: Portable, easy to use, mobile music and podcast consumption.
What are the key activities of entrepreneurs according to Byers et al. (2011)?
Entrepreneurs identify opportunities, mobilize resources, execute on their vision and manage risks.
Entrepreneurship is focused on the creation of a new enterprise that serves society and makes a positive change.
What is a Business Opportunity according to Dorf & Byers (2008)?
An opportunity is a timely and favorable juncture of circumstances providing a good chance for a successful venture.
Please name the nine categories of an opportunity (mentioned in the lecture).
- Increasing the value of a product or service
- New applications of existing means or technologies
- Creating mass markets
- Customization for individuals
- Increasing reach
- Managing the supply chain
- Convergence of industries
- Process innovation
- Increasing the scale of the firm
What are the characteristics of an attractive opportunity? Name and explain them shortly.
- Timely – a current need 📆
- Solvable – can be solved in the near future with accessible resources ➗
- Important – on the priority list of the customer :📢
- Profitable – adequate willingness to pay 💎
- Context – favorable regulatory and industry situation 💢
What is an entrepreneurial competence according to Tittel & Terzidis (2020)? What does competence consist of? Explain the different parts.
An entrepreneurial competence is the specific set of
- domain,
- relational and
- personal
competences needed to generate entrepreneurial action.
Name the six verbs that describe personal competence, according to Tittel & Terzidis (2020).
Be. Learn. Create. Want. Dare. Do.
What are the stages of Action Learning?
- Listen: Impulse
- Do: Activity & experience
- Reflect: what, how, why, how else
- Internalize: Theorize & practice
Session 2: Business Model & Strategy
How is strategy defined and what does strategic management deal with, according to Terzidis (2017)
A strategy is a plan or roadmap for the fundamental behavior of an organization in order to achieve its mission and long-term goals.
Strategic management deals with the initiatives taken by entrepreneurs involving the utilization of resources to enhance the performance of firms in their external environments.
Name the three key principles for strategic positioning (Porter, 2008).
- Strategy is the creation of a unique and valuable position, involving a different set of activities.
- Strategy requires you to make tradeffs in competing—to choose what not to do.
- Strategy involves creating “fit” (coherence) among a company’s activities.
What is the definition of a firm, according Coase (1937)?
A firm […] consists of the system of relationships which comes into existence when the direction of resources is dependent on an entrepreneur.
“The firm as a system” – in which markets is the firm embedded?
- Customer market,
- Labor market,
- Capital market,
- Supplier
- Complementary partners.
What is an industry, according to Byers and Dorf (2011)?
An industry is a group of firms producing products that are close substitutes for each other and serve the same customer.
Please describe the Industry Lifecycle and explain, if necessary, what is meant by the different phases.
- Emergence
- Limited growth
- Few competitors
- Growth
- Increased sales
- Good timing to enter the market
- Maturation
- Less growth
- Consolidation
- Decline
- Emergence
Please describe Porter’s Five Forces Model – name all the forces and differentiate between horizontal and vertical competition.
- Horizontal competition
- New entries can require more investment to stay competitive
- You must stand up to existing competition
- Substitute offerings can lure customers away
- Vertical competition
- Customers can force down prices by playing you and your rivals against one another.
- Powerful suppliers may constrain your profits if they charge higher prices.

- Horizontal competition
Give a definition of the term ‘business model’ according to Terzidis (2017).
A business model is an idealized and aggregated representation of how a firm creates value for all its stakeholders.
What are the business model V4 dimensions according to Al Debeiand Avison (2011)?
- Value Proposition
- The business logic of creating value for customers and/or to each party involved through offering products and services that satisfy the needs of their target segments.
- Value Network
- A way in which an organization enables transactions through coordination and collaboration among parties and multiple companies.
- Value architecture
- An architecture for the organization including its technological architecture and organizational infrastructure that allows the provisioning of products and services.
- Value Finance
- A way in which organizations manage issues related to costing, pricing, and revenue breakdown to sustain and improve its creation of revenue.
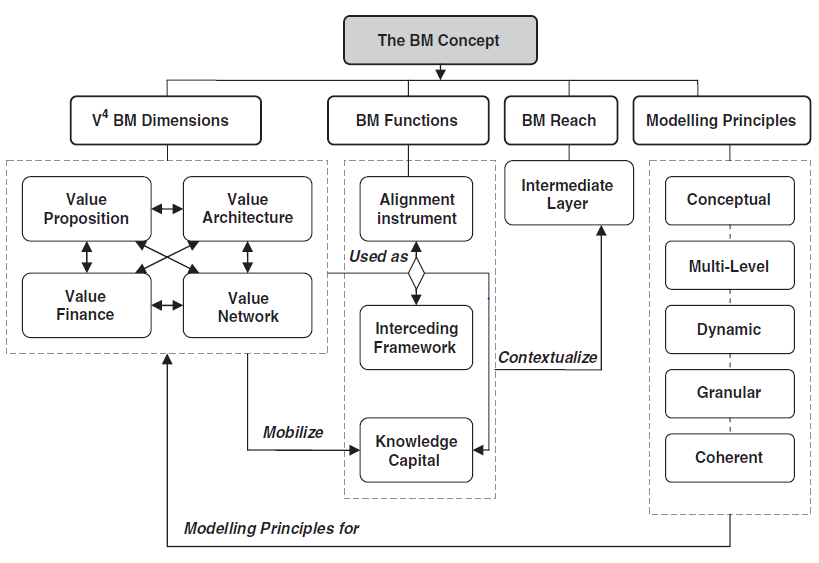
- Value Proposition
What are the Business Models Functions according to Al Debei & Avison (2011)?
- Alignment Instrument
- A theoretical tool of alignment providing a crucial instrument (i.e. bridge) for improving harmonization and consistency among strategy and business process including their supportive information systems.
- Interceding Framework
- A mediating construct or framework that connects technological potentials and innovations with the realization of economic value and the achievement of strategic outcomes.
- Knowledge Capital
- An intangible and tactical information/knowledge asset useful in supporting strategic decision-making functions, and thus valuable in providing the organization with an enduring competitive advantage.
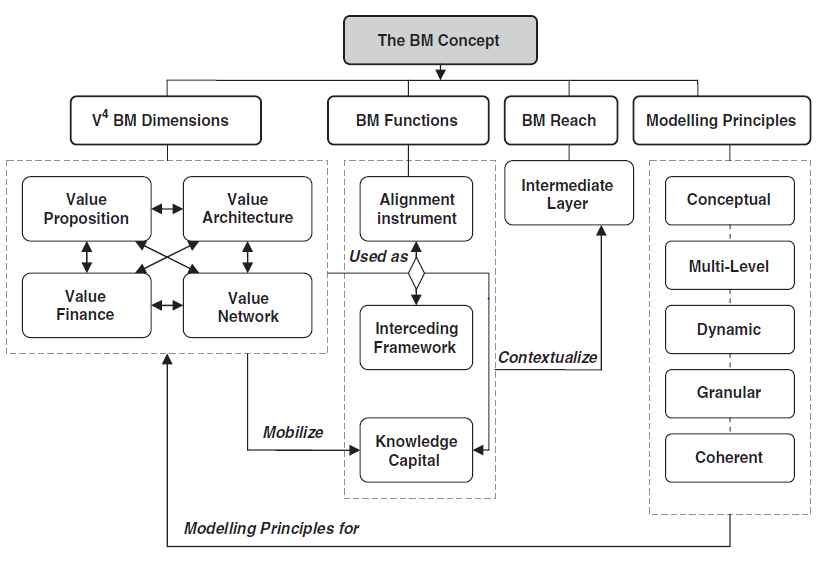
- Alignment Instrument
What is a model according to Stachoviak (1973)?
- Mapping
- A model is a representaiton of something
- Idealization
- A model is based on a justified abstraction and simplification. Not all elements of reality are mapped
- Pragmatism
- Models are used in concrete, pragmatic context
- Subjects (for whom?), for a concrete phase or period in time (when?), for certain operations like alignment, communication, and implementation (what for?)
- Mapping
Name the limitations of the Business Model Canvas.
- The purpose of the firm is not mentioned.
- Market structure and competitors are not mentioned.
- There is no explicit mentioning of the ‘value network’.
- Implication about the capital needs (e.g. need for working capital) are not mapped.
Name the ten rules for good Business Design.
1. Good business model design depends as much on art and intuition as it does on science and analysis.
2. Good business model design requires deep knowledge of customer needs and the technological and organizational resources that might meet those needs.
3. All good business models require an understanding of current business models at work in the market. Most new business model designs involve the hybridizations of others.
4. Alignment and coherence is desirable so that the business model elements will be mutually reinforcing.
5. Strategic analysis must be tied to business model design and vice versa. Strategy guides business model design and is also to some extent shaped by it.
6. Business models should be coupled with strategies and assets that make imitation difficult. Imitation will occur sooner or later, and pioneers must be fast learners.
7. Identifying the customer segment(s) to focus on first in order to learn and achieve proof-of-concept and business model viability is a critical capability.
8. When n-sided markets are involved, getting started early and effectively seeding the n sides is critical.
9. Good business model reengineering skills are an important component of strong dynamic capabilities. They enable proficient seizing.
10. The introduction of new business models into an existing organization is always difficult and may require a separate organizational unit.
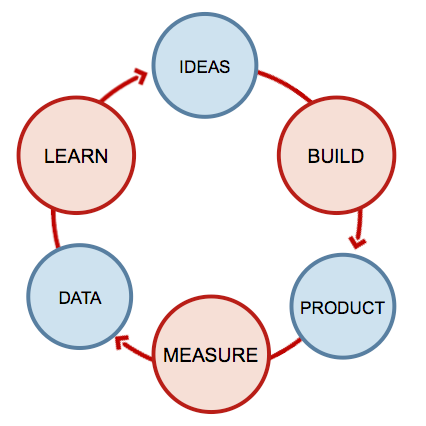
What is a Start-Up & what is a Lean Start-Up according to Ries (2011)?
A startup is a human institution designed to create a new product or service under conditions of extreme uncertainty.
Lean Startup is a method to systematically reduce the risk of projects with high uncertainty.
What is a Pivot according to Ries (2011)? Give an example and explain shortly.
A pivot is a structured course correction designed to test a new fundamental hypothesis about the product, strategy, and engine of growth.
Session 3: Marketing & Customer Development
Please name 5 top reasons why startups fail according to the lecture.
- No Market Need
- Run out of Cash
- Not the Right Team
- Got Outcompeted
- Pricing/Cost Issues
- User Un-friendly Product
- Product without a business model
- Poor Marketing
- Ignore Customers
Please give a definition of market, the actors who determine the market according to Homburg (2017)
A market is the place where a supply of products meets the demand for those products, which creates a price. This may occur in a real place (…) or in a virtual place (…).
Market activity is determined by the following actors: Buyers, Providers, Partners, State institutions and Interest groups.
Give a definition of marketing according to the American Marketing Association.
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Name the 4 P’s of the Marketing Mix according to Hisrich and Ramadani (2017). List at leas three examples, according to the Lecture.
- Product
- Function & features, quality, brand, design, warranty, packaging
- Price
- List price, discount, payment terms
- Promotion
- Advertising, personal selling, sales promotion publicity, direct marketing, events
- Place
- Distribution channels, locations, coverage, direct sales, web channels
- Product
Name the three Key Challenges of New Ventures and the explanation for each.
- Liablility of Smallness
- New ventures usually start off with few employees and limited financial resources. Their ability to sustain economic downtrends is limited. They encounter critical gaps in required skills. Smallness is negatively correlated with survival rates. (Aldrich & Auster 1986)
- Liability of Newness
- Stinchcombe (1965) argues liabilities of newness lead to higher failure rates of new firms compared to older ones. New firms have to create new processes, new relationships, and have a lack of reputation and experience. Clear empirical support (Freeman et al. 1983).
- Uncertaincy and Turbulence
- Uncertainty is directly connected to a valuable opportunity.
- Liablility of Smallness
What is market segmentation according to Wendell Smith (1956)?
Market segmentation involves viewing a heterogeneous market as a number of smaller homogeneous markets, in response to differing preferences, attributable to the desires of consumers for more precise satisfaction of their varying wants.
Name the different categories of Customers and list the three mentioned characteristics.
- Categories
- B2C: Business to Consumer
- B2B: Business to Business
- B2G: Business to Government
- B2H: Business to Healthcare
- Characteristics
- Customer facing processes are completely different
- Product definition, delivery, pricing is different
- Sales processes are different
- Categories
How is Value and the Value proposition defined in the lecture (inspired by Byers et al. 2011)
Value is the worth, importance, or usefulness to the customer. A value proposition is a promise of value to be delivered, communicated, and acknowledged.
What are the five dimensions of value of an offering according to Byers et al. (2011)?
- Product
- Price
- Access
- Service
- Experience
Please give the definition of a ‘job’ and its three characteristics according to the Job to be done theory (Ulwick 2016).
A job is the progress a customer seeks in a particular context. What do you want to achieve when you “hire“ a product or service?
Characteristics:
- A job is stable; it doesn’t change over time.
- A job has no geographical boundaries.
- A job is solution agnostic.
What is the desired outcome? Please rephrase the three listed descriptions of the lecture
- Desired Outcome Statements measure the success when getting a job done. ✅
- They describe how, in the view of the customer, it is possible to get the job done in a better way. ➕
- Desired Outcome Statements consist of:
- Direction of improvement ↗️
- Performance Metric ⏱️
- Object of control 🎮
- Context Clarifier 💢
What are the three approaches to determine the price of an offering?
- Value-based
- Competition-based
- Cost-based
What are the three steps of the Strategic Marketing Process?
- Segmentation
- Targeting
- Positioning
What are the five stages of innovation diffusion according to Roger (1983) and Moore (1991)?
- Innovators
- Early Adopters
- Early Majority
- Late majority
- Laggards
What are the four questions asked in the method described by van Westendorp (1976) What are the key statements of those?
- At what price would you consider the product to be so expensive that you would not consider buying it? (Too expensive)
- At what price would you consider the product to be priced so low that you would feel the quality could not be very good? (Too cheap)
- At what price would you consider the product starting to get expensive, so that it is not out of the question, but you would have to give some thought to buying it? (Expensive/High Side)
- At what price would you consider the product to be a bargain—a great buy for the money? (Inexpensive/Good Value)
Name the 8 listed methods according to the lecture to evaluate the market size.
- Market Reports and Estimates
- Top Down
- Sum of competitors
- Bottom Up
- Value Chain (Forward and Back)
- GDP Correlation
- Adjacent Market Method
- Social Media Analysis
What are the intended outcomes of a competitor analysis according to the lecture? Name the three listed outcomes.
- An understanding of your competitive environment,
- A positioning of your product and company in the competitive environment,
- Thus, enabling you to iterate your business model.
What are the six steps of the competitor analysis? Describe them briefly.
- Start
- Write down your company statement to start your analysis
- Set-up
- Specify the parameters for your analysis
- Identify your Competitors
- Think about companies in and outside your industry with the same technology, distribution, channel, production process, which solve the same problem
- Collect
- Collect the information specified using the determined sources and methods
- Present and Capture
- General information, Value Proposition/Network/Architecture/Finance
- Synthesize and Conclude
- Analyze the information draw your conclusions and develop your positioning
- Start
Session 4: IP & Technology Push
What is a patent (definition used in the lecture)?
A patent is an exclusion right of limited duration, which the state grants for the disclosure of an invention.
Name the three highlighted characteristics of a patent and the respective descriptions.
- Novelty: An invention is considered new if it is not state of the art (§ 3 sentence 1 PatG).
- Inventive activity: An invention requires an inventive step; it may not be obvious for an expert skilled in the art (§ 4 PatG).
- Industrial application: An invention needs to have an industrial application (§ 5 sentence 1 PatG).
What are the findings of patents according to Häussner et al. (2012)?
While preparing a patent application is costly and requires the disclosure of private information, patents have an important signaling value. (Häussner et al., 2012)
What are the three steps of a patent application?
- Filing
- Examination
- Infringement
Please name the different steps of the patent application process and assign it to the respective category. Also name all subitems with at least one description per category.
- Filing
- Heading and summary
- Name of the inventor & the invention, abstract of the technology
- Full Description
- Extensive description of the invention, function, potential uses
- Key Section: Patent Claims
- All attributes essential for realization of the invention
- Abstract formulation to ensure maximal protection
- Drawings
- Designs with explanations of the components in the description
- Heading and summary
- Examination
- Formal Examination
- Are the documents filled out correctly?
- Is the technology part of patent exclusions?
- Research (Optional)
- To which degree can the invention be protected?
- Examination
- Does the invention meet the criteria novelty, inventive step and industrial application?
- The disclosure happens automatically after 18 months.
- Thereafter, other companies can find the patent application and its technology.
- This happens whether the patent is finally granted or not.
- Competitors can file an opposition against the patent in the first nine months after the granting of the patent.
- Formal Examination
- Infringement
- Patent infringement lawsuit
- In regular court, not patent office.
- For the trial duration the patent is valid.
- Claims
- Injunctive relief (Unterlassungsanspruch)
- Claim for indemnity (Entschädigungsanspruch) on basis of the
- lost profit,
- the profit the infringing party made or
- costs for a license
- Patent infringement lawsuit
- Filing
What is excluded from patenting in Germany? Name three examples.
- Business ideas, plans and regulations
- Plant and animal species
- Unethical inventions
- Some inventions in microbiology, biotechnology and software can be patented
Please name three opportunities and three risks related to patenting.
- Opportunities
- Control over patent and invention
- Competitors cannot apply for the same patent: monopoly
- Reputation, Innovation, and higher valuation
- Communication & cooperation with partners
- Monitoring competitors through their patents
- Risks
- Disclosure of the invention after 18 months
- Application process expensive
- Maintenance expensive due to annual fees
- Enforcing patent infringements involves high legal expenses and lawyer costs
- Opportunities
What is the PCT? What does it provide? Please define as written in the lecture.
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) is an international patent law treaty, concluded in 1970.
It provides a unified procedure for filing patent applications to protect inventions in each of its contracting states.
What is a NTBF? Please define according to the lecture.
A New Technology-Based Firm (NTBF) is an entrepreneurial organization with the goal to actively create, develop, and/or commercialize offerings based on technology and/or research, particularly innovative products, processes, applications and services, which is no more than 12 years in operation.
Please name the Success Factors of New Ventures according to Song et al. (2008).
- Supply chain integration
- Market scope
- Firm age
- Size of founding team
- Financial resources
- Founders’ marketing experience
- Founders’ industry experience
- Existence of patent protection
What is technology push, according to the lecture?
Technology push is the development and market introduction of a new technology based product or service initiated by new technologies rather than customer needs.
What is market pull, according to the lecture?
Market Pull is the development and market introduction of a new product or service induced by customer demand.
What is a technology according to the lecture? Name all four subitems.
A technology is an artifact that performs a specific function by transforming, transporting or storing energy, matter or information.
Session 5: Leadership
How defines Terzidis (2021) Leadership and the leader, according to the lecture?
Leadership is organizing a group of people to achieve a common goal. A leader is somebody whom people follow, somebody who guides or directs others.
According to Luhmann (1995), what are the three characteristics of a Modern Organization?
- Membership
- Goals
- Hierarchies
What are the six traits, that are related to leadership (Northouse, 2016)?
Intelligence, Self-confidence, Determination, Integrity, Sociability, Emotional Intelligence
What are the five factor personality model dimensions that are related to leadership (Northouse, 2016)?
- high extraversion
- high conscientiousness
- high openness
- low neuroticism
- high agreeableness
What is the Basic Assumption of Transformational Leadership,Product according to Northouse (2016)?
Effective Leadership is a process that transforms people. Followers and leader are inextricably bound together in this transformation process.
Please name the six principles of effective leadership according to Malik (2006) and explain each one in your own words.
- Result orientation 🏁
- Contribution to the whole 🏗️
- Focus on few things 🔬
- Use strengths 💪
- Trust 🫂
- Think positive ➕
What are the five tasks of effective leadership according to Malik (2006)?
- Create goals
- Organize
- Decide
- Monitor
- Develop people
Please define the term ‘decision’ using the definitions of Mintzberg (1976) and the Gabler business dictionary (Wirtschaftslexikon).
A decision is a specific commitment to action (usually a commitment of resources).
Please name the 7 stages of a decision-making process according to Malik (2011).
1. Precise definition of the problem
2. Specification of the requirements & criteria the decision has to fulfill 3. Working-out the alternatives (all alternatives!)
4. Analysis of risks and consequences of all alternatives; setting limitations
5. Making the decision
6. Implementation plan
7. Establishment of feedback-loops: Follow-up and follow-through
What are the seven tools of effective leadership according to Malik (2011)?
- Meetings
- Reports
- Job Design
- Personal working methodology
- Budget
- Performance assessment
- „Waste disposal“
Session 6: Funding
Name the three forms of external financing mentioned in the lecture. For each of those, name the three outlined definitions.
- Equity capital
- Having a share implies to co-own the company
- Control rights, co-determination rights, information rights
- Direct participation in business success & failure
- Mezzanine capital
- Repayment obligation, profit linked interest
- Control rights, co-determination rights, information rights
- Potential participation in failiure
- Loans/Borrwed capital
- Repayment obligation, interest payment
- Investors do not hold any shares
- No participation in business success
- Equity capital
Please name all categories of internal financing for funding a start-up
- Self-financing
- Boot Strapping
What is the definition of risk (according to the Gabler Online Wirtschaftslexikon)?
A risk is an indication of the possibility that with some probability a loss may occur in connection with a decision or an expected benefit may not materialize.
What is the legal definition of Bankruptcy? Please name the main liability of the management, according to the Insolvency code.
A company is in a crisis, if it does not obtain loans at market prices anymore. It is then said to be ‘unworthy of credit’.
Bankruptcy (or insolvency) is a legal status of a firm that cannot repay the debts it owes to creditors.
Liability of the management: In this state, the management has no more than 3 weeks to file for insolvency by informing the court responsible.
What are the three reasons for insolvency (InsO §17-19)?
- Illiquidity (Zahlungsunfähigkeit)
- Imminent insolvency (Drohende Zahlungsunfähigkeit)
- Over-indebtedness (Überschuldung)
The risk of the investors depends on the type of investment: Please categorize the different types of external financing (diagram 1). Name the two definitions for each type. (Diagram 1: {High, medium, low}-risk)
- Equity capital
- Highest liability risk
- Lowest rank in case of insolvency or liquidation
- Mezzanine Capital
- Lower ranked than borrowed capital
- Higher interest rate than loans
- Loans/borrowed capital
- Reduced risk
- Highest rank in case of insolvency or liquidation
- Equity capital
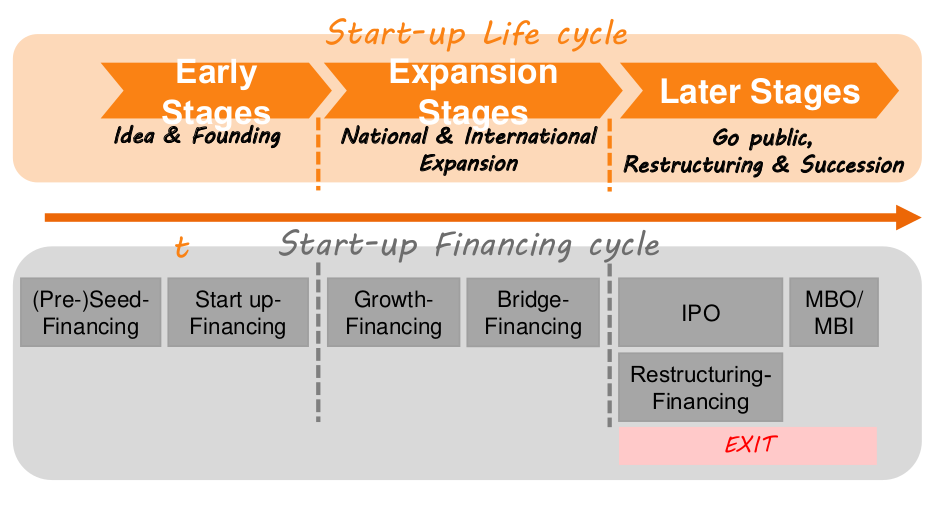
Early-Stages: Why is it difficult for start-ups to obtain loans according to Hof (2017)? Name all the mentioned aspects.
- Lack of securities
- No track record
- Irreversibility of R&D costs (sunk cost)
- Risk of failure
- High uncertainty about
- Market opportunities
- Development of the company
- Asymmetric information
- Skills of the founders? → no company history
- Difficulty to evaluate the quality of the product/technology
What are the characteristics of the Idea phase according to the lecture?
- Idea generation, prototyping, feasibility studies, team building etc.
- No revenues, no profits/moderate losses
- Financing from own cash-flows is not possible
What are the characteristics of the start-up phase according to the lecture?
- Company foundation, product development reaches production stage, first marketing concepts, partnerships
- First revenues, first small profits/high losses
- Rising capital requirements
What are the top five motivations of Business Angels for Investing, according to Brandenburger et al. (2012)?
- Supporting young entrepreneurs
- Contribute own professional experience
- For fun
- Potentially fruitful investment
- To play a role in the entrepreneurial process
Name the five top factors in the category Entrepreneur & Team, according to Brandenburger et al. (2012).
- Trustworthiness
- Enthusiasm
- Achievement motivation
- Ability to communicate the product
- Frustration tolerance
Name the six main phases of the funding process.
- Deal Origination
- Screening
- Evaluation
- Deal Closing
- Post-Investment Activities
- Exit
How do investors identify new companies, according to the lecture? Name three.
- Through direct contact from the entrepreneur (e.g., cold call, email, application platform).
- Through an active search for deals.
- Through a referral process.
Name and explain the several events an investor can make an exit through, according to Cumming & Macintosh (2003).
- Acquisition: the company as a whole is sold.
- Initial public offering (IPO): the investor sells the shares on the stock market.
- Buy-back: the investor sells the shares to the founders.
- Secondary sale: the investor sells shares to another investor.
- Write off: the investor realizes a capital loss.
How is a failure defined according to Gage (2012)?
If failure is defined as failing to see the projected return on investment say, a specific revenue growth rate or date to break even on cash flow, then more than 95% of start-ups fail.
Session 7: Business Plan
Explain the three mentioned reasons why it is necessary to have a business plan according to the lecture.
- Every major project needs a business plan. It is a roadmap and basis for funding decisions.
- Writing a business plan is an intensely focused activity. It requires honest thinking about your business concept.
- The more mature a business, the more you need a structured plan. Do not over-plan in the first phases.
What are the four key objectives of EXIST according to the lecture?
- Promote the huge potential for business ideas and entrepreneurs at universities and research institutions […].
- Establish a culture of entrepreneurship in university teaching, research and administration […].
- […] translate the findings of academic research into economic value […].
- […] increase the number of innovative business start-ups and create […] new jobs […]
Please name a typical structure of a business plan.
- Cover page and table of content
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Business environment analysis
- Industry background
- Competitive analysis
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
- Attachments and milestones
What are the four sections of the EXIST business plan template? (Gründerstipendium)
1. Executive Summary
2. Business Idea
3. Market/Competition
4. Operational Planning
Please explain the terms GbR, GmbH and UG according to the slides in the lecture.
- Gesellschaft bürgerlichen Rechts (GbR)
- Unlimited personal liability, no capital required
- Joint management (if not agreed differently)
- Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (GmbH)
- Limited personal liability, 25k€ minimum capital
- Notarial act for partners' agreement (Gesellschaftervertrag)
- Unternehmergesellschaft (UG)
- Start a GmbH with 1€
- 25% of profits must go into a reserve until the minimum initial capital of 25k€ has been reached
- Gesellschaft bürgerlichen Rechts (GbR)
What is the definition of Risk according to Vaughan (2008)?
Risk is a condition in which there is a possibility of an adverse deviation from a desired outcome that is expected or hoped for.
Please name the five points of the Consequence Scale, including the explanations.
1. Irrelevant—the risk doesn’t impact changes in the company’s goals and objectives
2. Minor—the risk can be treated with existing resources
3. Moderate—the impact of risk can be treated, but additional resources are required
4. Major—treatment of the risk will require significant additional resources from other sectors or sources
5. Significant—the risk might cause the company to fail achieving its goals and in some cases can prove to be fatal to the company
Please name the five points of the Likelihood Scale, including the explanations.
1. Rare—the risk might occur only in extraordinary circumstances. Such a risk has occurred somewhere else and might occur once in every 5+ years. Probability of occurrence is lower than 5%.
2. Unlikely—the risk might occur at some point, for example, once in 5 years. Probability of occurrence is 5–30%.
3. Possible—the risk might occur at some point, for example, once in 3 years. Probability of occurrence is 30–70%.
4. Likely—the risk might occur, at least once during the year. Probability of occurrence is 70–95%.
5. Almost certain—the risk is expected to occur in the majority of cases, occurs often during the relevant year. Probability of occurrence is 95–100%.
Please name the three options to treat risks, including the explanation, mentioned in the lecture.
- Risk avoidance includes taking proactive measures, such as requiring clients to cover purchased goods with credit through a collateral, or not undertaking any activities at all, which is expected to be damaging.
- Risk reduction includes taking concrete measures to minimize the consequences of a specific risk, such as installing alarms to secure assets from eventual thefts, or installing fire alarms.
- Risk anticipation, in literature, also known as the self-insurance strategy, where entrepreneurs leave aside some amount of money in order to cover damages if a risk occur.
Please name the steps of the Linear causation approach.
- analyze
- plan
- do
- check
- act
Please name the steps of the Linear causation approach in an entrepreneurial context.
- Market research
- Segmentation
- Positioning
- Business plan
- financing & staff
- “go live”
Please name and explain the five principle of effectuation according to Sarasvathy (2009)?
- Bird-in-Hand Principle
- As opposed to goal driven action, entrepreneurs take means driven action when building a new venture. Based on: who I am, what I know, and whom I know.
- Affordable Loss Principle
- As opposed to investing in calculations about expected returns, entrepreneurs limit risk by defining what they can afford to lose at each step. Then goals and actions are chosen where there is upside even if the downside ends up happening.
- Crazy Quilt Principle
- As opposed to determining the goal and then deciding who comes on board, entrepreneurs build partnerships with self-selecting stakeholders.
- By obtaining pre-commitments from these key partners early on in the venture, they reduce uncertainty and at the same time co-create the new market with its interested participants.
- Lemonade Principle
- As opposed to trying to avoid or overcome surprises or adapt to them, entrepreneurs invite the surprise factor.
- Instead of wasting time with creating “what-if” scenarios to deal with potentially happening worst-case situations, entrepreneurs leverage contingencies by interpreting “bad” news and surprises as potential clues to create new markets.
- Magnetron made chocolate melt…
- Pilot-in-the-Plane Principle
- As opposed to limiting entrepreneurial efforts to exploiting exogenous factors, entrepreneurs know their actions will result in the desired outcomes.
- So they focus on activities within their control
- This worldview is rooted in the belief that the future is neither found nor predicted, but rather made.
- Bird-in-Hand Principle